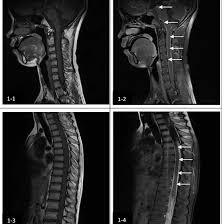
MRI For Medulla Plain
Book your MRI For Medulla Plain at Medifyhome, where we offer top-quality scans at the best prices. Our NABL & NABH accredited diagnostic centers ensure accurate and reliable results.
Book an Appointment
MRI For Medulla Plain
Medifyhome has collaborated with the best pathology laboratories that are NABL and NABH certified and follow ISO safety guidelines to provide the best MRI For Medulla Plain at an affordable price for needy individuals. The medulla oblongata can be described as being an important core within the brainstem which is just above the spinal chord though in most cases is below pons. Often referred to as the floor of the brainstem, it is the most inferior part and is involved in the regulation of several critical basic homeostatic functions necessary for human existence including breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. The medulla also acts as a relay for nerve impulses between the brain and spinal cord, therefore is part of the CNS. measuring about 3 cm in length the medulla oblongata is however an important region of the brain with functions that are essential in survival. It shelters centers that dictate simple reflexes for example swallowing, coughing and vomiting It is also involved in the relay of sensory data from the body. Another important part of the medulla is the group of centres that regulate the cardiovascular and respiratory systems contributing to maintaining the homeostasis of the organism. As part of the lower brain stem it is involved in many autonomic functions and relays and integrates sensory and motor pathways, this structure is critical in maintaining normal physiological activity. Cognition of this area if it can be through stroke, trauma, tumor, or neurodegenerative disease causes this area to pose severe health complications like breathing difficulty, irregular heart rate or paralysis.
To schedule an appointment for an MRI For Medulla Plain, simply contact Medifyhome or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.
What is an MRI?
The MRI is, therefore, a medical imaging technique that is used to make images of organs/tissues in the body. MRI is a technology that operates with strong magnets and radio waves in order to create images. According to this understanding, the MRT draws the hydrogen atoms in the body by dropping the magnetic field on them and through the radio waves interrupts this. And when the signal is switched off the hydrogen atoms release signals while getting back to normal position and these signals are used to build images. MRI uses high-resolution images that make it most suitable for capturing soft tissues, brain muscles and organs such as the thyroid gland. MRI is different from other techniques such as X-ray or computer tomography which utilise ionising radiation making MRI safer for many patients. MRI can be applied even to diagnose different disorders, such as tumours or flu, inflammation, and injuries. MRI is used to detect cancer, brain tumours, joint diseases, and spinal diseases. It can also be used to track the results of a disease or a treatment program.
What is the Medulla Plain?
Medulla oblongata is another part of the brainstem that is situated just above the spinal cord, but below the pons.NdEx
The medulla oblongata is a part of the lower brainstem at the top of the spinal cord. It establishes control of many important homeostatic reflexes in the body for instance, heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure to name but a few. This is a small region of the brainstem that links the brain to the spinal cord and through which all nerve signals pass on their way to the body.
Structural Description of the Medulla Oblongata
Location: The medulla oblongata is situated just above the spinal cord and below the pons which is in midline of the brainstem. It is the basal segment of the brainstem which is anatomically closely related to the spinal cord.
Size: It is measured to be about 3 cm in diameter or 1.2 inches and even though not very large, it is very significant for regulating simple survival processes.
Roles of the medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata contains vital centers of automatic reactions and is the point of switching of the signals between the brain and spinal cord.
Cardiovascular Regulation:
In the medulla, there are some portions, which control blood pressure and the rhythm of heart movements. This is achieved through the cardiac control centre,which is in the medullary nuclei namely, vasomotor centre, which involves the diameter of the blood vessels, therefore controlling the blood pressure.
Respiratory Regulation:
The medulla oblongata has important centers regulating the act of respiration, or breathing. These centers involve controlling the pattern and the rate of breathing depending on changes in the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood. Five general function control structures of the medulla are as follows; the dorsal respiratory group (DRG) and the ventral respiratory group (VRG).
Reflex Centers:
The medulla has control over some reflexes for example swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting. These are involuntary movements that help minimize injury to the body.
Why is MRI Crucial for Diagnosing Medulla Plain Conditions?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging is important for conditions involving medulla oblongata as it does help in providing the brain’s image by detecting this region and identifying the abnormalities of the region. Here’s why MRI is essential for diagnosing medulla oblongata conditions:
- Precision and Detail
The medulla oblongata is connected at the base of the brain and just below the pons. This area can be easily visualized with MRI since it provides a very detailed image and differentiation from surrounding structures in case there is any structural problem that is easily made.
- Detection of Stroke
Ischemic strokes are hemorrhagic strokes in the medulla oblongata that may lead to worst neurological complications. MRI is the most effective imaging modality to do both types of stroke because it will demonstrate viable parenchyma that has suffered from inadequate blood flow or hemorrhage.
- Tumors and Lesions
Benign or malignant tumours, cysts or any other growths can however arise on or near the medulla oblongata. MRI offer detailed images and we use it to determine the size, location and possible impacts on neighboring structures such as;the brainstem or even the spinal cord.
- Trauma and Injury
MRI scans are also useful in cases of traumatic brain injury mainly because damage in the medulla oblongata and other regions of the brainstem can be identified using MRI scans. This is specifically essential since disorder with brainstem produces risky hemiparesis that lasts for a long term, respiratory collapse, cardiovascular imbalance and loss of consciousness.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases and disorders
Another type of pathology that can influence the work of the medulla oblongata is multiple sclerosis or demyelizing diseases of the brainstem, and also ischemic injuries such as brainstem infarcts and various diseases of the central nervous system and their affected regions. MRI can assist in evaluating the overall disease course, identifying lesion and distinguishing between the pathological processes.
- Assessment of Cranial Nerves
It controls some important cranial nerves and is also responsible for the gasp reflex among other reflex arcs. Some of these included; any compression, inflammation or lesion on these nerves which can present as dysphagia or changes in speech or facial Paraesthesia.
How MRI Works for Medulla Plain Imaging
MRI is a type of imaging that uses strong magnets and radio waves to get clear images on internal structures for example medulla oblongata. Here’s a breakdown of how MRI works to image the medulla oblongata and other brain structures:
- Culture and Music
MRI mainly relies upon magnetic features of Hydrogen atoms which are fairly common in the body particularly water.
Brain tissues, including the medulla oblongata, are water dense, and therefore useful as antigens for MRI imaging of the head.
- Radiofrequency Pulses
After the hydrogen atoms are lined up by the magnetic field, the MRI machine then comes in with short blasts of radiofrequency (RF) signals. These pulses interfere for a moment with the coherent state of the hydrogen atoms within the body by spinning them out of phase.
- Relaxation and Signal Emission
When the RF pulse is switched off the hydrogen atoms tend to go back to their original state with the help of magnetic field. They also generate their own radiofrequency signals while they do so.
The emitted signals depend on the type of tissue and water content within the tissue; this enables the MRI machine to distinguish between different tissues with different characteristics.
- Tripod of Signal Detection and Image Reconstruction
In the case of the MRI scanner, the receiver coils are responsible for detecting those emitted signals to form the detailed images. These signals are then transformed by a computer into two or three dimensional representations of the brain structure such as the medulla oblongata.
- Contrast Imaging
At occasions, certain dyes are released into the bloodstream to help visualize particular features or disorders. These agents may be beneficial in indicating regions of abnormally perfused tissue, neoplasm or inflammation.
This contrast can cause the submission medulla oblongata and all the pathologies striking with higher contrast and definition around the tissues.
Conditions Detected by MRI in the Medulla Plain
Among the main functions the medulla oblongata controls respiration, heart rate, and the ability to swallow. Here are some common conditions that MRI can detect in the medulla oblongata:
- Ischemic Stroke or Brainstem Stroke
What it is: A stroke resulting from the blockage of blood vessels in the Medulla Oblongata is another type of stroke. Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke and it is subdivided into several categories this being one of them.
MRI detection: MRI especially with DWI is very sensitive to early ischemic changes. It can present decreased perfusion or tissue changes in the medulla.
Symptoms: Swallowing may become painful or impossible (dysphagia), there may be breathing difficulties and muscle weakness, even paralysis, and an inability to feel sensations in certain areas of the body.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke
What it is: A hemorrhagic stroke arises when a blood vessel in the medulla oblongata is burst and haemorrhage takes place within the highest part of the brainstem.
MRI detection: MRI in using either T2-weighted or gradient-echo sequences is practical for identifying hemorrhage since it outlines the areas of bleeding (e.g., blood clots).
Symptoms: Weakness that develops quickly; slurred speech; difficulty breathing; loss of alertness.
- Brainstem Tumors
What it is: The brainstem can be origin of the tumour or the tumour can originate from other organs of the body and spread to the brainstem.
MRI detection: MRI with contrast is recommended when searching for brainstem tumours. Tumors will be seen as a ring-structured masses with enhanced signal intensity and can well defined the localization and the extent of a lesion.
Symptoms: A headache and ataxia, cranial nerve palsies, and dysphagia.
- Multiple Sclerosis
What it is: Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease consisting of plaques or lesions in the central nervous system and also within the brainstem.
MRI detection: MRI is the most significant diagnostic technique for diagnosing MS, regardless of the manifestation type, T2 weighted and FLAIR are ideal sequences when an MS plaque within the brain stem including the medulla oblongata.
Symptoms: Automobile accidents, vision changes, muscle weakness, slurred speech, balance and coordination loss.
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
What it is: Injury to the brain stemming from trauma (e.g., from a car accident or fall) can affect the medulla oblongata, leading to bleeding, swelling, or direct injury.
MRI detection: T2-weighted and FLAIR MRI scans can help visualize contusions, hematomas, and brainstem swelling, especially in acute or subacute phases.
Symptoms: Loss of consciousness, respiratory problems, and motor dysfunction.
Benefits of MRI for Medulla Plain Imaging
The Medulla oblongata is an important component of the brainstem that regulates simple functions such as respiration, blood pressure and swallowing. Given this importance of this area, any pathological condition of this region can produce disastrous effects; therefore, precise anatomic detail is essential. Here are the key benefits of MRI for imaging the medulla oblongata:
- High Soft Tissue Contrast
Benefit: MRI can be especially beneficial in dissimilarating between various types of soft tissue because of its high contrast ratio. This is particularly true in imaging zones like the medullary where vessels, nerves, and nuclei among others are very sensitive and need to be visualized well.
- Non-invasive and Safe Imaging
Benefit: CT scans and X-Ray Radiation on the other hand uses ionizing radiation, therefore MRI is safer in cases where image repetitions are required, or for clients in sensitive categories.
- Detection of Small Lesions
Benefit: MRI is a very high spatial resolution that can help detect small lesions, tumor, stroke, or other abnormality in medulla oblongata and neighboring regions of the brainstem.
- Key findings of Acute and Chronic Pathologies
Benefit: MRI is very specific for both acute and chronic changes in the medulla oblongata area. For instance, it can detect an acute ischemic stroke with DWI and chronic changes such as atrophy of the brainstem or demyelination with T2WI and FLAIR.
- Mapping of Precise Structural Abnormality of the Blood Vessels
Benefit: MRI with MRA can show presence of the blood vessels in the brain and the pathology involving them like aneurysms, AVMs or vascular lesions in the brain stem, the medulla oblongata included.
- Test Type: MRI For Medulla Plain
- Preparation:
- Wear a loose-fitting cloth
- Fasting not required
- Carry Your ID Proof
- Prescription is mandatory for patients with a doctor’s sign, stamp, with DMC/HMC number; as per PC-PNDT Act
- Reports Time: With in 4-6 hours
- Test Price: Rs.4000
- How can I book an appointment for an MRI For Medulla Plain through Medifyhome?
To schedule an appointment for an MRI For Medulla Plain, simply contact Medifyhome or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.
- What does the term medulla oblongata mean?
The medulla is smaller than the pons and it is accommodated a bit above the spinal cord, right below the pons. It also regulates motor functions, osmoregulation, respiratory activities, vascular movements, and reflex actions that are indispensable for life.
- What are the duties of the medulla oblongata?
The medulla oblongata is responsible for several vital functions:
- Autonomic functions: It has mainly responsibilities for the control of heart rate, breathing rhythm and blood pressure.
- Reflexes: The medulla contains reflex centres for swallowing, coughing, vomiting and also sneezing.
- Sensory and motor pathways: I think it does something with sensory impulses and sends messages back and forth between the brain and the body.
- Cranial nerve functions: In the medulla, there are group points of several cranial nerves; these are the nuclei for the tasting for swallowing and speaking.
- Which of the cranial nerves are connected with the medulla oblongata?
Several important cranial nerves originate or have nuclei in the medulla:
- Cranial nerve VIII (Vestibulocochlear nerve): These nerves are concerned in hearing and balance.
- Cranial nerve IX (Glossopharyngeal nerve): Contribute to the perception of taste, swallowing, and secretion of salivary glands..
- Cranial nerve X (Vagus nerve): Regulates the functions of the parasympathetic category for example the rate of heartbeat, digestion and the respiratory system.
- Cranial nerve XII (Hypoglossal nerve): Looks after the faculties of speech and swallowing by means of complicated muscular movements of tongue.
- What occurs when medulla oblongata is affected?
Injury to the medulla oblongata could have severe effects because the structure is responsible for the regulation of life sustainment processes. Common effects of medullary damage include:
- Breathing problems (because the respiratory centres in the brain stem are impaired).
- Problems related to rate (as cardiovascular centers) involved).
- The loss of motor control (due to pathophysiology of motor pathways and some reflexes).
- Motor or sensory loss on one side of the body if the corticospinal tract is disrupted (motor pathway).
- What is pyramidal decussation?
The pyramidal decussation can be defined as the area of the medulla oblongata where the corticospinal tracts (motor nerve fibres from the cerebrum to the spinal cord) cross over from one side of the body to the other. This is why the left part of the brain manages the right side of the body and conversely; the right part of the brain manages the left side of the body.
- How does medulla oblongata play a role in respiration?
The medulla oblongata contain respiratory centers; the dorsal respiratory group (DRG) and ventral respiratory group (VRG). These centres control the rate and depth of the breathing depending on the amounts of Oxygen, and carbon dioxide in the blood. At any given time a body needs more O2, or is to expel CO2 it has in excess, the medulla modifies the frequency of breathing.
- What is their importance in the body?
The medulla contains important reflex centers that help the body respond to immediate, life-threatening conditions:
- Swallowing: Being coordinated by the swallowing center located in the medulla.
- Coughing and sneezing: Prevent foreign bodies, and irritants from getting into the respiratory system.
- Vomiting: Helps to protect the body through vomiting out bad products from the stomach. These reflexes are unconscious and necessary for the physical safeguard of the pers
Why Choose Medifyhome for MRI For Medulla Plain?
Medifyhome is an online medical consultant that provides home-based medical services not only in your area but also in most cities in India, including Hyderabad, Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, and more. We have collaborated with diagnostic centers that have the best machines and equipment to ensure you get accurate results. Medifyhome provides 24-hour customer service for booking the appointment of the services and guides you with instructions. Medifyhome also provides the best diagnostic centers at low prices. Once you receive your test results, you can easily book an appointment with our network of experienced doctors for consultation. To schedule an appointment for an MRI For Medulla Plain, simply contact Medifyhome or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.